Crack Wpa2 Bruteforce Vodafone Download
I hadn't ventured into Hackforums since a while, and this time when I went there I saw a thread about a script called Fluxion. It's based on another script called linset (actually it's no much different from linset, think of it as an improvement, with some bug fixes and additional options). I did once think about (and was asked in a comment about) using something like a man in the middle attack/ evil twin attack to get WPA password instead of going the bruteforce/dictionary route, but never looked the idea up on the internet nor spent much time pondering over it. However, once I saw the thread about this cool script, I decided to give it a try. So in this post I'll show you how I used Fluxion, and how you can too.
Fern Wifi Cracker is a Wireless security auditing and attack software program written using the Python Programming Language and the Python Qt GUI library, the program is able to crack and recover WEP/WPA/WPS keys and also run other network based attacks on wireless or ethernet based networks.
Disclaimer : Use this tool only on networks you own .Don't do anything illegal.
Step 1: Just Double Checking
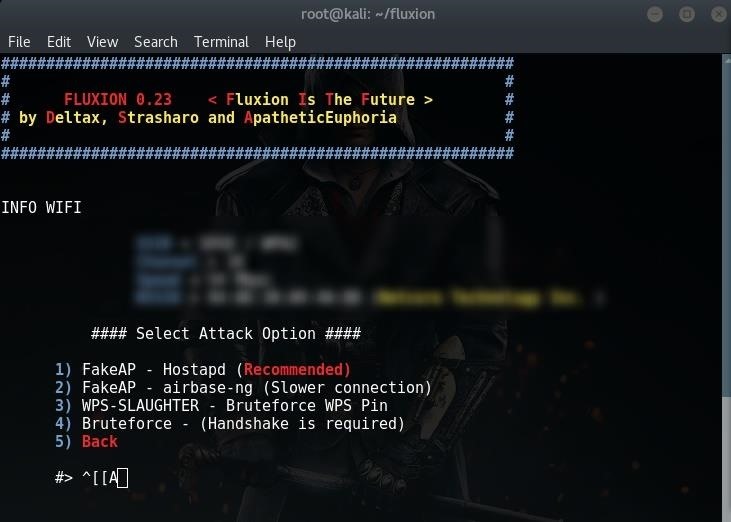
The first thing I did was make sure that Kali doesn't already have this tool. Maybe if you are reading this post a long time after it was written, then you might have the tool pre-installed in Kali. Cheap catv signal meter. In any case, try this out:
fluxion
cudaHashcat or oclHashcat
Wpa2 Password Crack
or Hashcat on KaliLinux got built-in capabilities to attack and decrypt or Cracking WPA2 WPA with Hashcat – handshake .cap files. Only constraint is, you need to convert a .cap file to a .hccap file format. This is rather easy.Hashcat is the self-proclaimed world’s fastest CPU-based password recovery tool. It is available free of charge, although it has a proprietary codebase. Versions are available for Linux, OSX, and Windows and can come in CPU-based or GPU-based variants. Hashcat currently supports a large range of hashing algorithms, including: Microsoft LM Hashes, MD4, MD5, SHA-family, Unix Crypt formats, MySQL, Cisco PIX, and many others.
Hashcat has made its way into the news many times for the optimizations and flaws discovered by its creator, which become exploited in subsequent hashcat releases. (For example, the flaw in 1Password’s hashing scheme)
Attack types
Hashcat offers multiple attack modes for obtaining effective and complex coverage over a hash’s keyspace. These modes are:- Brute-Force attack
- Combinator attack
- Dictionary attack
- Fingerprint attack
- Hybrid attack
- Mask attack
- Permutation attack
- Rule-based attack
- Table-Lookup attack
- Toggle-Case attack
Variants
Hashcat comes in two main variants:- Hashcat – A CPU-based password recovery tool
- oclHashcat – A GPU-accelerated tool
Hashcat is available for Linux, OSX and Windows. oclHashcat is only available for Linux and Windows due to improper implementations in OpenCL on OSX
Important Note: Many users try to capture with network cards that are not supported. You should purchase a card that supports Kali Linux including injection and monitor mode etc. A list can be found in 802.11 Recommended USB Wireless Cards for Kali Linux. It is very important that you have a supported card, otherwise you’ll be just wasting time and effort on something that just won’t do the job.
Why use Hashcat for cracking WPA WPA2 handshake file?
Pyrit is the fastest when it comes to cracking WPA2 WPA handshake files. So why are we using Hashcat to crack WPA2 WPA handshake files?- Because we can?
- Because Hashcat allows us to use customized attacks with predefined rules and Masks.
Hashcat allows you to use the following built-in
charsetsto attack a WPA2 WPA handshake file.Built-in charsets
Capture handshake with WiFite
WhyWiFite instead of other guides that uses Aircrack-ng ? Because we don’t have to type in commands.Type in the following command in your Kali Linux terminal:
root@kali:# wifite –wpa You could also type in
root@kali:#wifite wpa2 If you want to see everything, (
wep, wpa or wpa2, just type the following command. It doesn’t make any differences except few more minutesroot@kali:#wifiteOnce you type in following is what you’ll see.
So, we can see bunch of Access Points (AP in short). Always try to go for the ones with CLIENTS because it’s just much faster. You can choose all or pick by numbers. See screen-shot below
Awesome, we’ve got few with clients attached. I will pick 1 and 2 cause they have the best signal strength. Try picking the ones with good signal strength. If you pick one with poor signal, you might be waiting a LONG time before you capture anything .. if anything at all.
So I’ve picked 1 and 2. Press Enter to let WiFite do it’s magic.
Once you press ENTER, following is what you will see. I got impatient as the number 1 choice wasn’t doing anything for a LONG time. So I pressed CTRL+C to quit out of it.
This is actually a great feature of WIfite. It now asks me,
What do you want to do?
[c]ontinue attacking targets[e]xit completely.
c to continue ore to exit. This is the feature I was talking about. I typedc to continue. What it does, it skips choice 1 and starts attacking choice 2. This is a great feature cause not all routers or AP’s or targets will respond to an attack the similar way. You could of course wait and eventually get a respond, but if you’re just after ANY AP’s, it just saves time.And voila, took it only few seconds to capture a handshake. This AP had lots of clients and I managed to capture a handshake.
This handshake was saved in
Crack Wpa Wpa2
/root/hs/BigPond_58-98-35-E9-2B-8D.capfile.Once the capture is complete and there’s no more AP’s to attack, Wifite will just quit and you get your prompt back.
Now that we have a capture file with handshake on it, we can do a few things.
Cleanup your cap file using wpaclean
Next step will be converting the.capfile to a format cudaHashcat or oclHashcat or Hashcat on Kali Linux will understand.Here’s how to do it:
To convert your
.cap files manually in Kali Linux, use the following commandPlease note that the
wpaclean options are the wrong way round.<out.cap> <in.cap> instead of <in.cap> <out.cap> which may cause some confusion.In my case, the command is as follows:
Convert .cap file to .hccap format
We need to convert this file to a format cudaHashcat or oclHashcat or Hashcat on Kali Linux can understand.To convert it to
.hccap format with “aircrack-ng” we need to use the -J optionNote the
-J is a capitol J not lower case j.In my case, the command is as follows:
cudaHashcat or oclHashcat or Hashcat on Kali Linux is very flexible, so I’ll cover two most common and basic scenarios:
- Dictionary attack
- Mask attack
- Dictionary attack
First we need to find out which mode to use for WPA2 WPA handshake file. I’ve covered this in great length in Cracking MD5, phpBB, MySQL and SHA1 passwords with Hashcat on Kali Linux guide. Here’s a short rundown:
So it’s 2500.
Now use the following command to start the cracking process:
Bingo, I used a common password for this Wireless AP. Took me few seconds to crack it. Depending on your dictionary size, it might take a while.
You should remember, if you’re going to use Dictionary attack, Pyrit would be much much much faster than cudaHashcat or oclHashcat or Hashcat. Why we are showing this here? Cause we can. :)
2. Brute-Force Attack
Now this is the main part of this guide. Using Brute Force MASK attack.To crack WPA WPA2 handshake file using cudaHashcat or oclHashcat or Hashcat, use the following command:
Sample:
Where-m = 2500 means we are attacking a WPA2 WPA handshake file.-a = 3 means we are using Brute Force Attack mode (this is compatible with MASK attack).capture.hccap = This is your converted .cap file. We generated it using wpaclean and aircrack-ng.?d?d?d?d?d?d?d?d = This is your MASK where d = digit. That means this password is all in numbers. i.e. 7896435 or 12345678 etc.I’ve created a special MASK file to make things faster. You should create your own MASK file in similar way I explained earlier. I’ve saved my file in the following directory as
blackmoreops-1.hcmask.Do the following to see all available default MASK files provided by cudaHashcat or oclHashcat or Hashcat:
Sample .hcmask file
You can check the content of a sample.hcmask file using the following command:root@kali# tail -10 /usr/share/oclhashcat/masks/8char-1l-1u-1d-1s-compliant.hcmask
Edit this file to match your requirement, run Hashcat or cudaHashcat and let it rip.
Location of Cracked passwords
Hashcat or cudaHashcat saves all recovered passwords in a file. It will be in the same directory you’ve ran Hashcat or cudaHashcat or oclHashcat. In my case, I’ve ran all command from my home directory which is /root directory.Conclusion
This guide explains a lot. But you should read Wiki and Manuals from www.hashcat.net to get a better understanding of MASK and Rule based attacks because that's the biggest strength of Hashcat.Thanks for reading. Feel free to share this article.